An article for doctors diagnosing patients with a disease. It is not intended to replace a doctor's appointment or be used for self-diagnosis.
reason
- Flat feet can be divided into congenital and acquired conditions. Due to its presence, weight and pressure are distributed unevenly, resulting in deformation of the toe.
- Osteoporosis, characterized by loss of bone stiffness and low calcium levels.
- Obesity and being overweight can put excessive stress on bones, especially muscle weakness.
- When ligaments are weak, the genetic predisposition, as well as the characteristic changes in the foot (bunions), can be genetically predetermined.
- Wearing the wrong shoes. The problem often occurs in women due to walking in uncomfortable narrow heels. In this case, the correct loading of the foot is disrupted and the likelihood of hallux valgus deformity increases.
- Injuries, such as something heavy falling on the leg, a broken bone, or a bruise, can cause the foot to become deformed.
- Associated diseases of the endocrine system and nervous system.
- Hormones fluctuate dramatically, including during menopause, pregnancy, and during the natural course of the menstrual cycle.
stages and forms
- First stage -15°;
- II - 20°;
- III - 30°;
- IV - over 30°.
- Stage 1 - flat feet present but with slight deviation up to 15°;
- II - up to 23°;
- III - up to 30°;
- IV - the foot becomes completely flat with a deviation of more than 30°, which is considered a severe form.
- lung;
- average;
- Heavy.
- Structural, caused by congenital pathology;
- Static, caused by spinal curvature;
- Cramps due to overexertion or muscle tension;
- Traumatic foot deformity;
- Rickets etc.
As a result, there are many types of deformities in the first toe and other parts of the foot. To determine the characteristics of the course of the disease, it is necessary to consult a doctor and conduct examinations.
symptom
- fatigue when walking;
- corn;
- Calluses often appear in the same places;
- pain;
- Increased swelling of the lower limbs;
- Thumb to one side;
- Formation of characteristic bumps, often called "phalanges";
- The remaining toes deform and become hammertoes.
complication
- Bursitis, inflammation of the bursa. The problem manifests itself as swelling and pain in certain areas of the foot due to deformity of the foot joints.
- Arthropathy is the destruction of cartilage, resulting in reduced joint mobility, pain, and gait disturbance.
- The increased load causes wear and tear on the knee joint, increases pressure on the spine, and develops joint disease.
- The formation of heel spurs. In this condition, severe, almost unbearable pain occurs when walking.
- Achilles tendon bursitis and other diseases.
diagnosis
Instrumental methods
- If a problem with local circulation is suspected, ultrasound can identify disturbances in blood vessel function.
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging will help rule out other pathologies similar to bunions and obtain more detailed images of the disease.
- Plantar photography allows you to identify and determine the degree of flat feet.
- A plantar examination is an examination of the soles of the feet in a standing position.
- gout;
- Osteoarthritis;
- arthritis.
Modern medical clinics have the latest diagnostic equipment. This allows you to quickly identify a bunion and allow for a thorough examination and treatment.
Treatment of bunions
conservative approach
- Wear orthopedic shoes. It should be securely fastened, with a stable and low heel and extended toes. Additionally, special insoles, support pads, and other devices can be used to remove excess load from the metatarsal bones. It is important to understand that this treatment for bunions is usually long-term, lasting more than six months and sometimes even a year.
- Physical therapy sessions. Exercise therapy coaches select a program for a specific patient and teach the proper technique for performing the exercises. It is important to consult an expert during the first stages.
- Foot massage. It can only be performed in specialized medical centers, since its purpose is not relaxation, but the treatment of ectropion.
- Taking NSAIDs can both reduce the inflammatory process and relieve pain. It is important to consult a doctor before using such medications.
- Proper nutrition, a diet rich in calcium.
- sonophoria therapy;
- UHF;
- Magnet therapy.
surgical method
- on soft tissue. In this case, at an early stage of pathological development, it is possible to treat bunions in children and adults using the Silver and McBride techniques. They are associated only with the first stages of the disease.
- A combination of actions on bone and soft tissue structures to treat foot deformities, such as the Schede procedure.
- On the bone. This type of intervention is called an osteotomy, and there are several types. It is most commonly used in adults with moderate to severe foot deformities.
- Fast recovery time;
- No large cuts or seams;
- No long-term hospitalization required;
- The risk of complications is low.
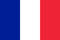
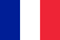
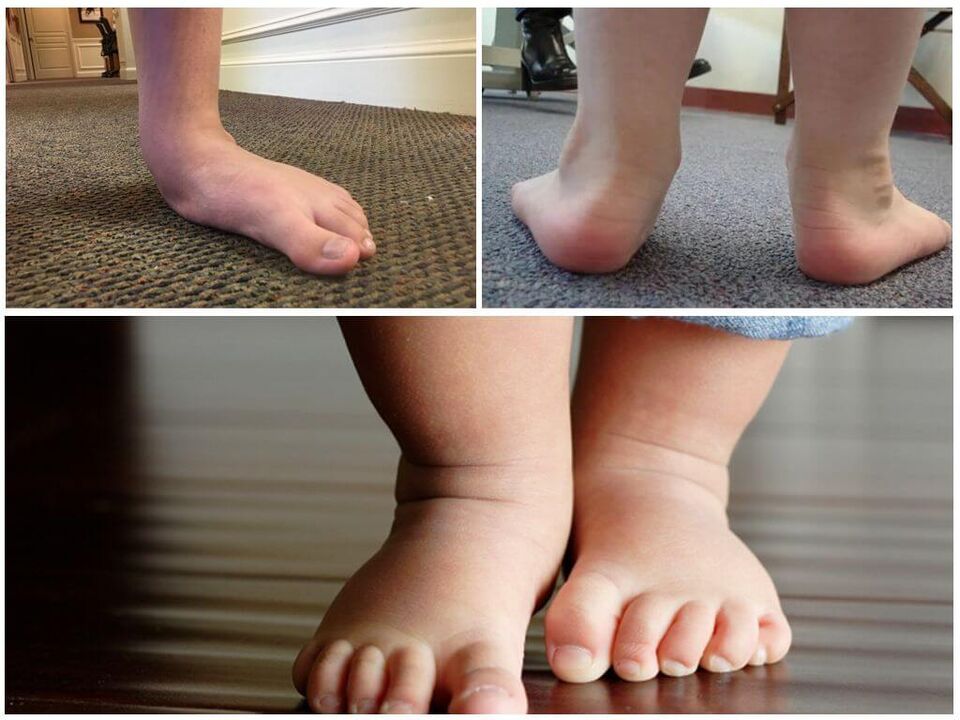
Children’s Treatment Features
Which doctor is treating you?
forecast
prevention
- Regular preventive examinations by an orthopedic traumatologist;
- Find and treat flat feet promptly;
- Wear comfortable shoes, excluding women's stilettos;
- Use orthopedic insoles if necessary;
- Control your weight and keep it in a normal and optimal state;
- Adhere to rest and work standards, especially if a person's occupational activities are associated with increased pressure on the legs;
- Eat proper and balanced nutrition and get rid of bad habits;
- Moderate physical activity, which means no physical inactivity and undue stress on the legs.